1
Consider the following statements regarding iron ores in India:
1. Magnetite is valued in the electrical industry due to its excellent magnetic qualities.
2. Hematite is the most important industrial iron ore in terms of quantity used, despite having a lower iron content than Magnetite.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Only 1
Both 1 and 2
Only 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Explanation: The provided text explicitly states that Magnetite has excellent magnetic qualities valuable for the electrical industry and that Hematite is the most important industrial iron ore by quantity used, with a slightly lower iron content (50-60%) compared to Magnetite (up to 70%). Therefore, both statements are correct.
2
Consider the following pairs regarding modes of mineral occurrence:
1. Alluvial Deposits : Gold
2. Decomposition of Surface Rocks : Bauxite
3. Sedimentary Rocks : Coal
4. Igneous Rocks : Lodes
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
One pair
Two pairs
All four pairs
Three pairs
Explanation: The text confirms all pairings. Alluvial deposits are called 'placer deposits' and contain minerals like gold. Bauxite is formed by the decomposition of surface rocks. Coal is found in beds or layers in sedimentary rocks. Lodes are larger occurrences of minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
3
Arrange the following states in descending order of their share in iron ore production for the year 2003-04, based on the given data.
1. Orissa
2. Jharkhand
3. Karnataka
4. Goa
1-3-4-2
3-1-4-2
3-1-2-4
1-2-3-4
Explanation: According to the 2003-04 data, the state-wise share in iron ore production was: Karnataka (26%), Orissa (25%), Goa (17%), and Jharkhand (12%). The correct descending order is Karnataka, Orissa, Goa, Jharkhand (3-1-4-2).
4
The Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt in Jharkhand is the leading producer of ______, a mineral indispensable in electric and electronic industries due to its excellent dielectric strength.
Bauxite
Copper
Limestone
Mica
Explanation: The text explicitly mentions that Mica is indispensable in electric and electronic industries due to its unique properties and that the Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt in Jharkhand is the leading producer.
5
Consider the following statements regarding energy resources in India:
1. Gondwana coal, which is over 200 million years old, is primarily located in the Damodar Valley.
2. Tertiary coal is found mainly in the northeastern states like Meghalaya and Assam.
3. Lignite, a low-grade brown coal, has its principal reserves in Neyveli, Tamil Nadu.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1 and 2 only
2 and 3 only
All of the above
1 and 3 only
Explanation: All three statements are correct based on the text. Gondwana coal is in the Damodar Valley. Tertiary coal is in the northeastern states. Lignite reserves are in Neyveli (Tamil Nadu).
6
Assertion (A): India needs to focus on the conservation of mineral resources.
Reason (R): Mineral resources are finite, non-renewable, and the current consumption rates are far greater than the rates of replenishment.
In the context of the above two statements, which one of the following is correct?
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Explanation: The text states the need for conservation precisely because mineral resources are finite and non-renewable, and their consumption outpaces their formation. Thus, the reason correctly explains the assertion.
7
The Bailadila range of hills, known for super high-grade hematite iron ore, is located in which state?
Orissa
Chhattisgarh
Jharkhand
Karnataka
Explanation: The text identifies the Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt and specifically mentions that the Bailadila range of hills is in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh.
8
Nearly ______ of manganese is required to manufacture one tonne of steel.
Explanation: The text states, "Nearly 10 kg of manganese is needed to produce one tonne of steel."
9
What is 'Rat-hole' mining, as described in the provided text?
A modern, government-regulated mining technique for narrow mineral veins.
A form of illegal mining conducted in national parks.
A term for mining slurry and waste.
Family-based coal mining in long, narrow tunnels, particularly in Meghalaya.
Explanation: The text describes 'Rat-hole' mining as a practice in Meghalaya where coal mining is done by family members in long, narrow tunnels because minerals are owned by individuals or communities.
10
Which of the following locations are mentioned as sites for experimental geothermal energy projects in India?
1. Madhapur, near Bhuj
2. Parvati Valley, Himachal Pradesh
3. Puga Valley, Ladakh
4. Nagarcoil, Tamil Nadu
1 and 4 only
1, 2, and 3
2 and 3 only
2, 3, and 4
Explanation: The text specifies two experimental geothermal projects: one in Parvati Valley near Manikaran (Himachal Pradesh) and another in Puga Valley (Ladakh). Madhapur is mentioned for a solar plant, and Nagarcoil for wind energy.
11
According to the 2003-04 data, which state was the largest producer of Bauxite in India?
Gujarat
Jharkhand
Orissa
Maharashtra
Explanation: The data table for Bauxite production shows Orissa as the largest producer with a 45% share.
12
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of aluminium mentioned in the text?
Magnetic properties
Extreme lightness
Good conductivity
Malleability
Explanation: The text describes aluminium as having strength, extreme lightness, good conductivity, and malleability. Magnetic properties are associated with Magnetite iron ore, not aluminium.
13
Which geographical region of India is described as being almost devoid of economic minerals?
The Peninsular Rocks
The Western and Eastern flanks of the peninsula
The North Indian Alluvial Plains
The Aravalli ranges
Explanation: The section on the distribution of minerals explicitly states that the "North Indian Alluvial Plains are almost devoid of economic minerals."
14
The 1700 km long Hazira-Bijaipur-Jagdishpur (HVJ) pipeline is primarily associated with the transport of which energy resource?
Petroleum
Slurry of iron ore
Natural Gas
Coal
Explanation: The text identifies the Hazira-Bijaipur-Jagdishpur (HVJ) pipeline as a 1700 km long gas pipeline that links offshore fields with industrial complexes.
15
Consider the following statements about Copper in India:
1. India has abundant reserves and production of copper.
2. The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh are a significant producer of copper.
3. The Khetri mines in Rajasthan are famous for copper.
Which statements are correct?
1 and 2 only
1 and 3 only
All are correct
2 and 3 only
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect; the text says India is "critically deficient" in copper reserves and production. Statements 2 and 3 are correct as the text mentions Balaghat and Khetri mines as significant producers.
16
Minerals found in the sands of valley floors and at the base of hills, such as gold and silver, are known as ______ deposits.
Explanation: The text defines these alluvial deposits as ‘placer deposits’.
17
Which type of coal is considered the highest quality hard coal?
Peat
Lignite
Anthracite
Bituminous
Explanation: Under the 'Types' of coal, Anthracite is described as "the highest quality hard coal."
18
Which area accounts for the largest share (63%) of India's petroleum production?
Mumbai High
Gujarat
Assam
Krishna-Godavari basin
Explanation: The text provides a breakdown of major production areas by share, stating that Mumbai High contributes 63%.
19
Limestone is the basic raw material for the ______ industry and is essential for smelting iron ore in a blast furnace.
chemical
electrical
paint
cement
Explanation: The text clearly states that limestone "is the basic raw material for the cement industry".
20
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a strategy for the conservation of minerals?
Using mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner.
Promoting the export of raw minerals to generate revenue.
Recycling of metals and use of scrap metals.
Using other substitutes for minerals.
Explanation: The conservation strategies listed are sustainable use, improving technology for low-grade ores, recycling, and using substitutes. Promoting exports would accelerate depletion, not conserve resources.
21
Consider the following table regarding mineral production shares (2003-04):
| 1. Manganese |
Orissa |
33% |
| 2. Copper |
Madhya Pradesh |
58% |
| 3. Bauxite |
Gujarat |
17% |
| 4. Limestone |
Rajasthan |
15% |
How many of the above pairings are correctly matched as per the provided data?
One pair
All four pairs
Two pairs
Three pairs
Explanation: Based on the state-wise share tables provided in the text for 2003-04, all four pairings are correct. Orissa led in Manganese (33%), Madhya Pradesh in Copper (58%), Gujarat was a major producer of Bauxite (17%), and Rajasthan was a major producer of Limestone (15%).
22
The Monazite sands of which state are rich in Thorium, a fuel used for nuclear energy?
Rajasthan
Jharkhand
Kerala
Tamil Nadu
Explanation: The text states that for nuclear energy, "The Monazite sands of Kerala are also rich in thorium."
23
Hydroelectricity is a ______ source of energy, while thermal electricity, generated from fossil fuels, is a ______ source.
renewable, non-renewable
non-renewable, renewable
conventional, non-conventional
non-conventional, conventional
Explanation: The section on electricity generation explicitly describes hydroelectricity (from fast-flowing water) as a renewable resource and thermal electricity (from burning fossil fuels) as a non-renewable resource.
24
Which of the following minerals is classified as a 'Precious' metallic mineral in the provided text?
Copper
Bauxite
Gold
Manganese
Explanation: The classification table lists gold, silver, and platinum as examples of 'Precious' metallic minerals.
25
What is the geological definition of a mineral provided in the text?
A combination of various rocks found in the earth's crust.
Any substance that can be mined for economic profit.
A homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
A hard, crystalline substance formed by evaporation.
Explanation: The first sentence of the text defines a mineral as "a homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure."
26
Consider the following statements about the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India:
1. GST is an origin-based tax, meaning the tax revenue goes to the state where goods are produced.
2. It is a comprehensive, value-added tax levied on the supply of goods and services.
3. The Constitution (101st Amendment) Act, 2016, provided the legislative basis for GST.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1 and 2 only
3 only
2 and 3 only
All of the above
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect; the text specifies that GST is a destination-based consumption tax. Statements 2 and 3 are correct as per the description and legislative basis provided in the text.
27
Regarding the GST Council, what is the voting power distribution between the Centre and the States, and what majority is required for a decision?
Centre 1/2, States 1/2; Simple majority.
Centre 2/3, States 1/3; 2/3rd majority.
Centre 1/3, States 2/3; 3/4th majority.
Centre 1/3, States 2/3; Simple majority.
Explanation: The text clearly states that in the GST Council, "The Centre holds 1/3rd of the votes, and states hold 2/3rd. Decisions require a 3/4th majority."
28
The ______ is levied by the Centre on inter-state supplies of goods and services and on imports.
Explanation: The text defines the dual GST model, where IGST (Integrated GST) is levied by the Centre on inter-state supplies and imports.
29
Which of the following taxes was NOT subsumed under GST?
Service Tax
Central Excise Duty
Customs Duty on imports
State VAT
Explanation: The text states that Customs duty is still collected on imports alongside IGST and is listed as being outside GST. Service Tax, Central Excise Duty, and State VAT were all subsumed.
30
Match the tax concept with its description:
| 1. Progressive Tax |
A. Tax burden is ultimately borne by final consumers. |
| 2. Indirect Tax |
B. Tax rates increase with the taxable amount. |
| 3. Impact of Tax |
C. The point where the tax's economic burden is felt. |
| 4. Incidence of Tax |
D. The point where the tax is initially imposed. |
Which is the correct matching?
1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D
1-A, 2-B, 3-D, 4-C
1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
Explanation: Based on the definitions: Progressive tax rates increase with value (1-B). Indirect tax burden is shifted to consumers (2-A). The impact is where the burden is felt (3-C). The incidence is the point of imposition (4-D).
31
Following the 2019 corporate tax reforms, what is the new base tax rate for a new manufacturing company registered after October 1, 2019, with a turnover less than ₹400 cr?
Explanation: The table on Corporate Tax Rate Changes shows that the new base rate for new manufacturing companies under the specified conditions is 15%.
32
What is the primary purpose of the Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT)?
To tax agricultural income.
To tax long-term capital gains.
To ensure 'zero tax' companies showing high book profits pay a minimum tax.
To replace the Dividend Distribution Tax.
Explanation: The text defines MAT as a tax imposed on 'zero tax' companies that show high "book profits" but little taxable income, to ensure they pay a minimum amount of tax.
33
With the abolition of the Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) from FY 2020-21, how are dividends now taxed?
They are taxed in the hands of the shareholders as part of their personal income.
They are completely tax-free.
They are taxed at a flat rate of 15% for all shareholders.
They are taxed in the hands of the company at the new corporate rate.
Explanation: The section on DDT states that after its abolition at the company level, "dividends are taxed in the hands of the shareholders as part of their personal income, according to their respective income tax slabs."
34
For shares and equity mutual funds, what is the holding period beyond which a sale results in a Long-Term Capital Gain (LTCG)?
36 months
12 months
24 months
6 months
Explanation: The text specifies that for shares and equity mutual funds, the holding period for a Short-Term Capital Gain (STCG) is 12 months or less, meaning a holding period of more than 12 months results in an LTCG.
35
What was the primary flaw of the pre-GST indirect tax system, which led to inflated final prices?
Regressive taxation
Lack of fiscal autonomy for states
Excessively high tax rates on essential goods
The cascading effect (tax on tax)
Explanation: The text explicitly mentions the "Cascading Effect" as a flaw of the pre-GST system, where taxes were levied on a value that included previous taxes, inflating final prices.
36
Which of the following items is mentioned in the text as being currently kept outside the GST framework?
Luxury cars
Alcoholic liquor for human consumption
Pan masala
Processed food products
Explanation: Under "Items outside GST," the first item listed is "Alcoholic liquor for human consumption."
37
Which of the following is highlighted as a key benefit of GST for the states?
Increased fiscal autonomy to set tax rates independently.
Access to tax revenue from the fast-growing services sector.
Guaranteed revenue increase for manufacturing-heavy states.
The ability to cross-utilize CGST and SGST credits.
Explanation: The "Benefits and Advantages of GST" section lists "Access to tax revenue from the fast-growing services sector" as a key advantage for the States.
38
Which of the following is NOT listed as a challenge of the GST system?
Potential revenue loss for manufacturing states.
Acceleration of economic formalization.
Reduced fiscal autonomy for states.
The complexity of a multi-tier tax structure.
Explanation: The text lists revenue loss, reduced fiscal autonomy, and complexity as challenges. Acceleration of formalization is listed under "GST Performance and Impact" as a positive outcome, not a challenge.
39
What is the purpose of the 'E-Way Bill' system introduced under GST?
To provide a digital platform for filing GST returns.
To issue electronic invoices to consumers.
To monitor the transportation of goods and deter tax evasion.
To settle tax disputes between the Centre and states.
Explanation: Under "Compliance Initiatives," the E-Way Bill is described as an "Electronic bill for transporting goods to deter misreporting."
40
According to the provided table for the new simplified personal income tax regime (FY 2020-21), what is the tax rate for an individual with an income of ₹8 lakh?
Explanation: The table shows the income slab of ₹7.5 lakh - ₹10 lakh is taxed at 15% under the new regime.
41
Consider the following statements:
1. Corporate Income Tax is an indirect tax levied on the profits of companies.
2. Personal Income Tax in India is an example of progressive taxation.
3. MAT credit can be carried forward for up to 15 years.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
1 and 2 only
1 and 3 only
2 and 3 only
All are correct
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect; Corporate Income Tax is a direct tax. Statement 2 is correct as Indian income tax is a typical example of progressive taxation. Statement 3 is also correct, as the text specifies that MAT credit can be carried forward for up to 15 years.
42
The 'Vivad se Vishwas' scheme launched in 2020-21 was aimed at reducing litigation in which area?
Indirect taxes (GST)
Direct taxes
Corporate disputes under the Companies Act
Land and property disputes
Explanation: The text mentions this scheme under "Compliance Initiatives" and states it was launched "to reduce litigation in direct taxes".
43
Data from GST filings has provided valuable insights into India's internal trade, which is estimated to be about ______ of its GDP.
Explanation: Under the "GST Performance and Impact" section, the text notes that GST data reveals internal trade is "estimated to be about 60% of GDP."
44
Based on the provided table comparing corporate tax rates with ASEAN countries, which country has a corporate tax rate of 17%?
Vietnam
Singapore
Thailand
Malaysia
Explanation: The comparison table clearly shows Singapore with a corporate tax rate of 17%.
45
A tax where the incidence and impact fall on the same person is known as a(n) __________.
Indirect Tax
Regressive Tax
Direct Tax
Proportional Tax
Explanation: The definition given for a Direct Tax is "A tax where the incidence and impact fall on the same person."
46
In the context of India's 1991 economic reforms, what does the "P" in the LPG framework stand for and what path of reform does it represent?
Planning; representing the direction of reform.
Policy; representing the goal of reform.
Privatisation; representing the path of reform.
Public Sector; representing the focus of reform.
Explanation: The text defines the LPG framework where P stands for Privatisation, which "represents the path of reform" through the transfer of state assets to the private sector.
47
Which of the following was a key conditionality imposed by the IMF on India to manage the 1991 Balance of Payment crisis?
A 22% devaluation of the rupee.
Increasing the peak import tariff to 200%.
Nationalisation of all private banks.
An increase in government expenditure by 10%.
Explanation: The text lists several IMF conditions, one of which was the "Devaluation of the rupee by 22%."
48
The Third Generation of economic reforms, announced with the Tenth Plan, was primarily focused on what objective?
Dismantling the Administered Price Mechanism.
Making the Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) fully functional for inclusive growth.
Promoting de-licensing of industries.
Developing an information technology-enabled India.
Explanation: The text specifies that the Third Generation reforms committed to making "the Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) fully functional to ensure that the benefits of reform reached the grassroots level."
49
Which of the following statements accurately reflects a key reason for replacing the Planning Commission with NITI Aayog?
The Planning Commission was not a constitutional body.
The Five-Year Plans had consistently failed to achieve their growth targets.
There was a need for a body that fosters 'Cooperative Federalism' with active state involvement.
The government wanted to return to a fully state-led imperative planning model.
Explanation: The rationale for NITI Aayog's establishment highlights the need for a body that would nurture an environment based on "Cooperative Federalism" and involve states as active partners, a shift from the centralized approach of the Planning Commission.
50
Who comprises the Governing Council of the NITI Aayog?
Only the Prime Minister and the Vice-Chairperson.
The Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories.
The Prime Minister, cabinet ministers, and the CEO.
Experts from various fields nominated by the President.
Explanation: The structure of NITI Aayog described in the text states that the Governing Council comprises "the Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories."
51
The "Bombay Plan" of 1944-45, which advocated for rapid industrialization with a focus on heavy industries, was prepared by whom?
M. Visvesvaraya
The Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI)
A group of eight leading Indian capitalists
M.N. Roy
Explanation: The text attributes the Bombay Plan to "Eight leading Indian capitalists, including J.R.D. Tata and G.D. Birla".
52
The _______ Plan, formulated by Sriman Narayan Agarwal in 1944, emphasized agriculture, cottage industries, and a decentralized economic structure.
People's
Sarvodaya
Gandhian
Bombay
Explanation: The text identifies the Gandhian Plan as being formulated by Sriman Narayan Agarwal with an emphasis on agriculture and decentralization.
53
The Fifth Five-Year Plan (1974-1978) laid significant stress on which two objectives?
Rapid industrialisation and public sector growth.
Modernisation of industries and WTO membership.
Employment and poverty alleviation (garibi hatao).
Growth with stability and the Green Revolution.
Explanation: The description of the Fifth Five-Year Plan states that it "laid significant stress on employment and poverty alleviation (garibi hatao)."
54
Consider the following statements:
1. The First Five-Year Plan was based on the Mahalanobis Model.
2. The Third Five-Year Plan is considered a "miserable failure" due to wars with China and Pakistan.
3. The Eighth Five-Year Plan promoted the modernisation of industries and was launched after the 1991 reforms.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1 and 2 only
2 and 3 only
3 only
All of the above
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect; the First Plan was based on the Harrod-Domar Model. Statement 2 is correct, as the plan was hampered by two wars. Statement 3 is correct, as the Eighth Plan was launched in 1992 and focused on modernizing industries.
55
The nationalisation of 14 major Indian banks and the Green Revolution were two landmark economic events that occurred during which Five-Year Plan?
Second Five-Year Plan
Third Five-Year Plan
Fifth Five-Year Plan
Fourth Five-Year Plan
Explanation: The text explicitly mentions that during the Fourth Five-Year Plan (1969-1974), "two landmark economic events defined this period: the nationalisation of 14 major Indian Banks and the Green Revolution."
56
Why did the Indian government declare "plan holidays" after the Third Five-Year Plan?
Due to a shift in economic policy towards a free market.
To prepare for the launch of the Green Revolution.
Due to the severe failure of the plan, hampered by two wars.
Because of a change in government and political instability.
Explanation: The text states that the "miserable failure" of the Third Plan, which was hampered by wars, "led the government to declare 'plan holidays' for the subsequent years."
57
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was established during which Five-Year Plan?
Fifth Plan
Sixth Plan
Seventh Plan
Eighth Plan
Explanation: The description of the Sixth Five-Year Plan (1980-1985) states that a "major institutional achievement was the establishment of the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)".
58
Match the Five-Year Plan with its theme/slogan:
| 1. Fourth Plan |
A. 'Garibi Hatao' |
| 2. Fifth Plan |
B. "Faster, More Inclusive and Sustainable Growth" |
| 3. Twelfth Plan |
C. "Rapid and more inclusive growth" |
| 4. Eleventh Plan |
D. "Growth with stability" |
Which is the correct matching?
1-A, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B
1-D, 2-B, 3-A, 4-C
1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
Explanation: Based on the text: Fourth Plan emphasized "growth with stability" (1-D). Fifth Plan focused on "garibi hatao" (2-A). Twelfth Plan's theme was "Faster, More Inclusive and Sustainable Growth" (3-B). Eleventh Plan's theme was "rapid and more inclusive growth" (4-C).
59
The "Washington Consensus" that emerged in the early 1980s advocated for which economic strategy?
A state-led planned economy with protectionist policies.
A minimal role for government, promoting privatization and liberalization.
A mixed economy with a balance between state and market.
A focus on agriculture and cottage industries.
Explanation: The text describes the Washington Consensus as a strategy that "advocated for a minimal role for the government" and promoted privatization and liberalization.
60
What does the guiding principle of 'Antyodaya' for NITI Aayog signify?
Fostering cooperative federalism.
People's participation in development.
Harnessing India's demographic dividend.
Upliftment of the poor, marginalised, and downtrodden.
Explanation: The text defines the 'Antyodaya' principle as prioritizing the "service and upliftment of the poor, marginalised and downtrodden."
61
According to the text, what is the WTO's definition of Globalisation?
The transfer of state assets to the private sector.
An increase in economic integration among nations via unrestricted cross-border movements of goods, services, capital, and labour.
The reduction of state influence in the economy.
The process of aligning domestic prices with international prices.
Explanation: Globalisation, the ultimate goal of reforms, is defined as an increase in economic integration leading to "unrestricted cross border movements of goods and services, capital and the labour force."
62
The Right to Education Act, which made education free and compulsory for children aged 6-14, was introduced during which Five-Year Plan?
Ninth Plan
Eleventh Plan
Tenth Plan
Twelfth Plan
Explanation: The text notes that a landmark achievement of the Eleventh Five-Year Plan (2007-2012) was "the introduction of the Right to Education Act in 2009".
63
The process of selling shares of state-owned enterprises is referred to as ______, which is a form of Privatisation.
Liberalisation
Globalisation
Disinvestment
Corporatisation
Explanation: The text defines Privatisation and explains that it can occur through denationalisation or, more commonly, through "disinvestment, which is the selling of shares of state-owned enterprises."
64
The Second Five-Year Plan, which focused on rapid industrialisation, was drafted under the leadership of whom?
K.N. Raj
P.C. Mahalanobis
Jawaharlal Nehru
D.P. Dhar
Explanation: The text states that the Second Five-Year Plan was "drafted under the leadership of P.C. Mahalanobis".
65
The "Rolling Plan" model, where effectiveness is evaluated annually and new plans are created, was introduced in India during which period?
1966-1969
1990-1992
1978-1980
2000-2002
Explanation: The text describes the Rolling Plan model being used during the period of political instability from 1978-1980 by the Janata Party government.
66
India's economic reform program, initiated in 1991, is distinguished by its emphasis on a ______ transition, in contrast to the "shock therapy" seen in other countries.
rapid and revolutionary
state-dominated
gradual and evolutionary
foreign-funded
Explanation: The introduction to Economic Reforms notes that India's program "is distinguished by its emphasis on a gradual and evolutionary transition, in contrast to the 'shock therapy'".
67
Which of the following is a key function of NITI Aayog that distinguishes it from the former Planning Commission?
Allocating the Plan Budget to states.
Serving as a knowledge and innovation hub.
Acting as the 'economic Cabinet of the country'.
Approving the final draft of the Five-Year Plans.
Explanation: Among NITI Aayog's key functions is to serve as a "Knowledge and Innovation Hub" and a repository of research, a role that differs from the Planning Commission's focus on resource allocation and plan formulation.
68
The 1991 economic crisis in India was exacerbated by which international event?
The fall of the Soviet Union.
The first Gulf War.
The East Asian financial crisis.
The formation of the World Trade Organisation.
Explanation: The text states that "The 1991 crisis was exacerbated by the first Gulf War, which caused a spike in oil prices and a drop in private remittances".
69
What was the main focus of the First Five-Year Plan (1951-1956)?
Rapid industrialisation
The agrarian sector, including dams and irrigation
Poverty alleviation
Modernisation of industries
Explanation: The text clearly states that the main focus of the First Five-Year Plan "was the agrarian sector, including significant investments in dams and irrigation."
70
What was the theme of the Twelfth Five-Year Plan (2012-2017), the final plan in the series?
"Growth with stability"
"Faster, More Inclusive and Sustainable Growth"
"Rapid and more inclusive growth"
"Garibi Hatao"
Explanation: The text specifies that the Twelfth Five-Year Plan was themed "Faster, More Inclusive and Sustainable Growth".
71
പര്യടനത്തിലിരിക്കുന്ന ഒരാൾ മണിക്കൂറിൽ 64 കിലോമീറ്റർ വേഗതയിൽ 160 കിലോമീറ്റർ സഞ്ചരിക്കുന്നു. അടുത്ത 160 കി. മീ. മണിക്കൂറിൽ 80 കി. മീ. സഞ്ചരിക്കുന്നു. എങ്കിൽ ആദ്യ 320 കിലോമീറ്റർ ടൂറിന്റെ ശരാശരി വേഗത എത്ര?
36.55 km/hr
36 km/hr
72 km/hr
71.11 km/hr
Explanation: ശരാശരി വേഗത = 2𝑥𝑦𝑥+𝑦=2×64×8064+80=6409=71.11
72
വിലയിരുത്തുക
(−2)6(−4)−7((−2)2)−5
ഇവയൊന്നുമല്ല
\( 2^{-18} \)
\( 2^{30} \)
\( -2^{2} \)
Explanation: \( \frac{(-2)^{6}(-4)^{-7}}{((-2)^{2})^{-5}} = \frac{(-2)^{6}(-1\times 2^{2})^{-7}}{(-2)^{-10}}\)
\( \frac{(-2)^{6}(-1^{-7})\times (2^{-14})}{(-2)^{-10}} \)
\( \frac{(-1^{6})\times(2)^{6}(-1)\times (2^{-14})}{(-2)^{-10}} \)
\( \frac{-1\times2^{-8}}{-1^{-10}\times2^{-10}} \) \( = - 2^{-8 +10} =- 2^{2} = -2\times-2 = +4 \)
73
10 നിരീക്ഷണങ്ങളുടെ ശരാശരി 20 ആണെന്ന് കണ്ടെത്തി. 12 എന്നത് 21 എന്ന് തെറ്റായി വായിച്ചതായി പിന്നീട് കണ്ടെത്തി. ശരിയായ ശരാശരി ?
22.2
20.9
19.1
33.3
Explanation: തെറ്റായ ശരാശരി - 20
ആകെ തുക \( = 20\times10 = 200 \)
പുതിയ തുക = 200-21+12 = 191
പുതിയ ശരാശരി \( = \frac{191}{10} = 19.1 \)
74
ഒരു ഓഫീസിലെ 80% ജീവനക്കാരും സ്ത്രീകളാണ്. ആകെ പുരുഷ ജീവനക്കാരുടെ എണ്ണം 25 ആണ്. എങ്കിൽ സ്ത്രീ ജീവനക്കാരുടെ എണ്ണം എത്ര?
9
125
100
115
Explanation: 20 % \( \times X = 25 \) , X = ആകെ ജീവനക്കാരുടെ എണ്ണം
\( X = \frac{25\times100}{20} = 125 \)
സ്ത്രീ ജീവനക്കാരുടെ എണ്ണം \( = 125 - 25 = 100 \)
75
\( a:b::c:d \)എങ്കിൽ, ഇനിപ്പറയുന്നവയിൽ ഏതാണ് ശരി?
\( ac = bd \)
\( ab = cd \)
ഇവയൊന്നുമല്ല
\( ad = bc \)
Explanation: \(a:b=c:d\)
= \(\frac{a}{b}= \frac{c}{d}\)
= \(\frac{a+b}{a-b}=\frac{c+d}{c-d}\)
\(\frac{a}{c}=\frac{b}{d} = ad = bc\)
എന്നാൽ ഈ അംശബന്ധത്തെ \(ab=cd, ac = bd\) എന്ന് എഴുതാൻ സാധിക്കില്ല.
76
2,12,36,80,?,252,392
150
145
136
123
Explanation: 12+13=2
22+23=12
32+33=36
42+43=80
52+53=150
62+63=252
72+73=392
77
2022-ലെ കലണ്ടർ ഏതു വർഷത്തെ കലണ്ടറിനു സമാനമായിരിക്കും ?
2033
2032
2031
2030
Explanation:
\( 2022\div 4 \) ചെയ്യുമ്പോൾ, ശിഷ്ടം 2 അല്ലെങ്കിൽ 3 വന്നാൽ അതേ കലണ്ടർ ആവർത്തിക്കുന്നത് 11 വർഷം കഴിഞ്ഞുള്ള കലണ്ടർ ആയിരിക്കും.
അതായത്, 2022 +11 = 2033
2033 ലെ കലണ്ടർ 2022-ലെ കലണ്ടറിനു സമാനമായിരിക്കും.
78
നൽകിയിരിക്കുന്ന ഓപ്ഷനുകളിൽ ഒറ്റയാനെ തിരിച്ചറിയുക.
101
103
107
105
Explanation: 105 ഒഴികെ തന്നിരിക്കുന്ന മറ്റെല്ലാ സംഖ്യകളും അഭാജ്യ സംഖ്യകളാണ്.
അതുകൊണ്ട് ഉത്തരം 105.
79
4 : 10 ന് ക്ലോക്കിന്റെ രണ്ട് കൈകൾക്കിടയിലുള്ള കോൺ കണ്ടെത്തുക.
55°
65°
68°
61°
Explanation: \( \theta= \frac{11}{2}m -30h \) <br> =\(\frac{11}{2}\times10 -30 \times 4\) = 65\(^{\circ}\)
80
If CHAIR is coded as 34567 and RENT is coded as 7128, how would REAR be written in the same code?
1751
7157
7137
1731
Explanation: 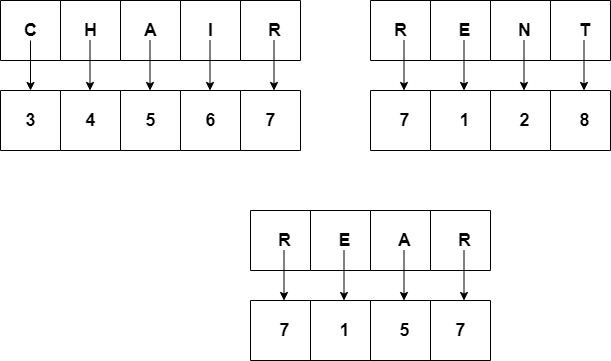
81
Choose the correctly spelt word from the following.
Righteous
Pronounciation
Momento
Guage
Explanation:
- Gauge : to measure or determine the amount, quantity, size, condition, etc, of. 2. to estimate or appraise; judge.
- Memento : an object kept as a reminder of a person or event.
- Pronunciation : The act or manner of pronouncing words; utterance of speech.
82
She is relieved __ her duty.
Off
Of
In
From
Explanation:
- The preposition “of” can be used in many different contexts.
- It can be used to help quantify a time or measurement (e.g., “the fifth of September” or “three pounds of potatoes”) and even identify a location (e.g., “south of California”), but it can also create more general relationships between objects and their nouns.
lethargic
ideal
indolent
idle
Explanation:
- ideal : satisfying one's conception of what is perfect; most suitable.
- idle : to run at low power and often disconnected usually so that power is not used for useful work
- indolent : wanting to avoid activity or exertion; lazy.
- lethargic : affected by lethargy; sluggish and apathetic.
84
Choose the correct sentence.
Ideal
Lethargic
Thirty thousand dollars is a huge amount
Everyone of the girls love to have gifts
Explanation:
- In order for a sentence to be grammatically correct, the subject and verb must both be singular or plural. In other words, the subject and verb must agree with one another in their tense. If the subject is in plural form, the verb should also be in plur al form (and vice versa).
- So, Thirty thousand dollars is a huge amount is the right answer.
sheep-sheep
louse-louses
loaf-loafs
echo-echo
Explanation:
- The plural of loaf is loaves.
- The plural form of louse is lice.
- The plural form of echo is echoes.
- The plural form of sheep is sheep.
86
The more you try, the ___ it is.
Good
Better
Best
Worst
Explanation:
- Option B is the right answer.
- The more you try, the better it is.
87
I am wrong in this case, ___
aren’t I ?
amn’t I ?
am I ?
are I
Explanation:
- Question tags are formed with the auxiliary or modal verb from the statement and the appropriate subject.
- A positive statement is followed by a negative question tag.
- A negative statement is followed by a positive question tag.
88
Their ___ is different and the best in this field.
modus operandi
bona fide
nota bene
ad infinitum
Explanation:
- A modus operandi is someone's habits of working, particularly in the context of business or criminal investigations; but also more generally, it is a Latin phrase, approximately translated as mode of operating.
- Nota bene is a Latin phrase meaning "note well".
- Ad infinitum is a Latin phrase meaning "to infinity" or "forevermore".
- bona fide : genuine; real.
89
Dr. Salim Ali was a naturalist and an \(\underline { \space expert \space on \space bird }\)
expert on birds.
Find a one word substitute for
the underlined set of words.
philanthropist
ophthalmologist
ornithologist
orthodontist
Explanation:
- ornithologist : a person who studies or is an expert on birds.
- Sálim Moizuddin Abdul Ali, better known as Dr. Sálim Ali, born on 12th November, 1896, was the pre-eminent ornithologist of India, famously known as the “Birdman of India”. When Sálim was ten years old, his uncle presented him with an air-gun.
90
When the police ___, the thief had already left.
Was coming
Came
Has come
Come
Explanation:
- The given sentence is in past perfect tense.
- Eg : The train had just left when I arrived at the station.
- She had just left the room when the police arrived.
- I had just put the washing out when it started to rain.
91
നെന്മണി -ശരിയായി പിരിച്ചെഴുതുന്നത് എങ്ങനെ ?
നെൽ + മണി
നെൻ + മണി
നെന്മ+ അണി
നെല്ല് + മണി
Explanation: ആദേശസന്ധി
- ഒരു വർണം പോയി അതിന്റെ സ്ഥാനത്ത് മറ്റൊരു വർണം വരുന്നതാണ് ആദേശം. വ്യഞ്ജനങ്ങൾ തമ്മിൽ ചേരുന്നിടത്താണ് മിക്കപ്പോഴും ആദേശം വരുന്നത്.
നെന്മണി എന്ന പദം പിരിച്ചെഴുതുമ്പോൾ നെല്+മണി എന്നോ നെൽ+മണി എന്നോ ആണ് വരിക. ‘ല്’ എന്നു പിരിച്ചാലും ‘ൽ’ എന്നു പിരിച്ചാലും അതുപോയി ന്, ൻ എന്നിവയിൽ ഒന്നുവരും.
കണ്ണീർ കൺ+നീർ; നീർ എന്നതിലെ ‘ന’ പോയി അതിന്റെ സ്ഥാനത്ത് ‘ണ’ വരും. വിണ്ടലം പിരിച്ചാൽ വിൺ+തലം എന്നുവരും. തലം എന്നതിലെ ‘ത’ പോയി അതിനുപകരം ‘ട’ വരും. അങ്ങനെ വിൺ+തലം വിണ്ടലമാകും.
92
കവി എന്ന പദത്തിന്റെ എതിർലിംഗം ഏത് ?
കവയത്രി
കവിയത്രി
കവിയിത്രി
കവയിത്രി
Explanation:
- യാചകൻ = യാചകി
- കാഥികൻ = കാഥിക
- പതി = പത്നി
- ജനകൻ = ജനനി
- ലേഖകൻ = ലേഖിക
- പണ്ഡിതൻ = പണ്ഡിത
- മാടമ്പി = കെട്ടിലമ്മ
- കൈമൾ = കുഞ്ഞമ്മ
- അച്ഛൻ = അമ്മ
- ശിവൻ = ശിവാനി
- കവി = കവയിത്രി
93
'യാഥാർഥ്യം അവഗണിച്ച് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുക '- എന്നർത്ഥം വരുന്ന ശൈലി ഏത് ?
കലക്കവെള്ളത്തിൽ മീൻ പിടിക്കുക
കൊത്തും കോളും നോക്കുക
കണ്ണടച്ച് ഇരുട്ടാക്കുക
ഒഴുക്കത്ത് വാലാട്ടുക
Explanation:
- എണ്ണിക്കഴിക്ക - ഉത്കണ്ഠാപൂർവ്വം കാത്തിരിക്കുക
- ഏട്ടിലെ പശു - പ്രയോഗസാധ്യമല്ലാത്ത വിജ്ഞാനം
- ഏറാൻ മൂളുക - എല്ലാം സമ്മതിക്കുക
- കാനൽജലം - തോന്നൽ മാത്രം
- കിണറ്റിലെ തവള - ലോകപരിജ്ഞാനം കുറഞ്ഞ ആൾ
- മുയൽ കൊമ്പ് - ഇല്ലാത്ത വസ്തു
- വനരോദനം - നിഷ്പ്രയോജനമായ സങ്കടം പറച്ചിൽ
- സിംഹാവലോകനം - ആകെ കൂടി നോക്കുക
94
ശുദ്ധമായ വാക്യം തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുക .
മത്സരവിജയികൾക്ക് മൂന്ന് പുസ്തകം വീതം കൊടുത്തു
മത്സരവിജയികൾക്ക് മൂന്ന് പുസ്തകം കൊടുത്തു
മത്സരവിജയികൾക്ക് മുമ്മൂന്ന് പുസ്തകം വീതം കൊടുത്തു
മത്സരവിജയികൾക്ക് മൂന്ന് പുസ്തകങ്ങൾ കൊടുത്തു
Explanation: താഴെ തന്നിരിക്കുന്ന ഉദാഹരങ്ങളിൽ ആദ്യത്തെ വാക്യo തെറ്റും രണ്ടമത്തേത് അതിന്റെ ശരിയായ വാക്യവുമാണ്.
രാമു ആദ്യവും പിന്നീട് രാജുവും വന്നു ചേർന്നു.
ആദ്യം രാമുവും പിന്നീട് രാജുവും വന്നു ചേർന്നു.
അവൾ സ്ഥലത്ത് ഇല്ലാത്തതിനാലും നീ വരാത്തതു കൊണ്ടും കാര്യം നടന്നില്ല.
അവൾ സ്ഥലത്ത് ഇല്ലാത്തതിനാലും നീ വരാത്തതിനാലും കാര്യം നടന്നില്ല .
കുട്ടികൾക്ക് പഠിക്കുന്നതിനും കളിക്കാനുമുള്ള അവസരങ്ങൾ നൽകേണ്ടതാണ് .
കുട്ടികൾക്ക് പഠിക്കുന്നതിനും കളിക്കുന്നതിനും അവസരങ്ങൾ നൽകേണ്ടതാണ്.
ബന്ധുക്കളെ കാണുന്നതിനും കാര്യങ്ങൾ പറയാനും സൗകര്യമുണ്ട് .
ബന്ധുക്കളെ കാണുന്നതിനും കാര്യങ്ങൾ പറയുന്നതിനും സൗകര്യമുണ്ട് .
95
കാട്ടുമനുഷ്യൻ എന്നത് താഴെ കൊടുത്തിരിക്കുന്നതിൽ ഏതിന്റെ ഒറ്റപ്പദം ആണ് ?
കാട്ടിൽ നിന്ന് വരുന്ന മനുഷ്യൻ
കാടു കൊണ്ട് ഉപജീവനം കഴിക്കുന്ന മനുഷ്യൻ
കാട്ടിൽ ജനിച്ചു വളർന്ന മനുഷ്യൻ
കാട്ടിൽ ജീവിക്കുന്ന മനുഷ്യൻ
Explanation:
- വ്യാകരണം പഠിച്ചിട്ടുളളവൻ – വൈയാകരണൻ
- ഉണർന്നിരിക്കുന്ന അവസ്ഥ – ജാഗരം
- ഋഷിയെ സംബന്ധിക്കുന്നത് – ആർഷം
- കുടിക്കാനുള്ള ആഗ്രഹം – പിപാസ
- ഗ്രഹിക്കുന്ന ആൾ – ഗ്രാഹകൻ
- വിജയത്തെ ഘോഷിക്കുന്ന യാത്ര – ജൈത്രയാത്ര
- ഭക്ഷിക്കാനാഗ്രഹിക്കുന്നയാൾ – ബുഭുക്ഷ
- വാതിൽ കാവൽക്കാരി – വേത്രവതി
- ആശ നശിച്ചവൻ – ഭഗ്നാശൻ
96
കടൽ എന്ന് അർഥം വരുന്ന മറ്റൊരു പദം ഏത് ?
ശാർദ്ദൂലം
അശ്മം
വാജി
അർണവം
Explanation:
- അതിഥി- ആഗന്തുകന്, ഗൃഹാഗതന്, വിരുന്നുകാരന്.
- അവല്- ചിപിടകം, പൃഥുകം, ചിപിടം.
- ആമ- കൂര്മം, കച്ഛപം, കമഠം.
- അവയവം- അംഗം, അപഘനം, പ്രതീകം.
- പക്ഷിക്കൂട്- പഞ്ജരം, നീഡം, കുലായം.
97
താഴെ കൊടുത്തിരിക്കുന്നതിൽ ശരിയായ പദം തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുക ?
അസ്തിക്കൂടം
അസ്ഥിക്കൂടം
അസ്തികൂടം
അസ്ഥികൂടം
Explanation: തെറ്റായ രൂപം - ശരിയായ രൂപം
- അകമ്പിടി - അകമ്പടി
- അംഗവീരൻ - അങ്കവീരൻ
- അച്ചുതൻ - അച്യുതൻ
- അത്ഭുതം - അദ്ഭുതം
- അധ്യാപിക - അദ്ധ്യാപിക
- ഉത്ഘാടനം - ഉദ്ഘാടനം
- എഴുന്നെള്ളുക - എഴുന്നള്ളുക
- കബന്ദം - കബന്ധം
- ജഡായു - ജടായു
- തത്വം - തത്ത്വം
98
'പ്രശാന്തം' എന്ന പദത്തിന്റെ വിപരീത പദം ഏത് ?
നിശാന്തം
പ്രദോഷം
പ്രക്ഷുബ്ധം
നിർദോഷം
Explanation:
വക്രം x ഋജു
പ്രത്യക്ഷം x പരോക്ഷം
ദ്രുതം X മന്ദം
ധാരാളംX വിരളം
നക്തം X ദിവം
നന്മ X തിന്മ
നമ്രം X ഉന്നമ്രം
നിന്ദ X സ്തുതി
നിന്ദ്യം X ശ്ലാഘ്യം
നിമേഷം X ഉന്മേഷം
നിയതം X അനിയതം
നിഷേധ്യം X അനിഷേധ്യം
പരകീയം X സ്വകീയം
നിന്ദ x സ്തുതി
99
'കൊടുത്തു + ഇല്ല' - ചേർത്ത് എഴുതിയതിൽ ശരിയേത് ?
കൊടുത്തതില്ല
കൊടുത്തുഇല്ല
കൊടുത്തീല
കൊടുത്തില്ല
Explanation:
- മരം + ഇല് = മരത്തില്
- പൊല് + പൂ = പൊല്പ്പൂ
- തിരു + ഓണം = തിരുവോണം
- മടി + ശീല = മടിശ്ശീല
- കല് + മദം = കന്മദം
100
‘Many a mickle (little) makes a mickle’ ഇതിനു സമാനമായ പഴഞ്ചൊല്ല് ഏത് ?
അധികമായാൽ അമൃതും വിഷം
ഉപ്പോളം വരുമോ ഉപ്പിലിട്ടത്
അച്ചാർ കൂടിയാൽ സദ്യ കേമം
പലതുള്ളി പെരുവെള്ളം
Explanation:
- ആളേറിയാൽ പാമ്പ് ചാവില്ല -Too many cooks spoil the broth
- അധികമായാൽ അമൃതും വിഷം- Too much of anything is good for nothing
- ആഴമുള്ള ജലത്തിൽ ഓളമില്ല - Still waters run deep
- നേരില്ലാത്തിടത്തു നിലയില്ല - A lie has no legs
